Introduction
This articles gives a quick overview of mapping points between FAFB14 (as used by the “walled garden” and Virtual Fly Brain and FlyWire.
Basic point mapping
Some known points
# identified location in FAFB14
p.fafb.nm <- cbind(477042, 284535, 90680)
p.fafb.raw <- p.fafb.nm/c(4,4,40)
# corresponding location in FlyWire
p.flywire.raw <- cbind(118865, 71338, 2267)
p.flywire.nm <- p.flywire.raw * c(4,4,40)Compare displacements (in nm) for forward or inverse mapping
# check displacement
flywire2fafb(p.flywire.nm)-p.fafb.nm
#> X Y Z
#> [1,] 3 -1 0
# check what happens when you apply the inverse
fafb2flywire(p.fafb.nm)-p.flywire.nm
#> X Y Z
#> [1,] -3 2 0A sample neuron. First map the points
data("AV4b1", package='catmaid')
before=xyzmatrix(AV4b1)
after=fafb2flywire(before)Then some stats and a quick histogram
d=sqrt(rowSums((before-after)^2))
summary(d)
#> Min. 1st Qu. Median Mean 3rd Qu. Max.
#> 2.0 287.9 416.0 446.9 559.1 2113.7
hist(d, br=20, main='Displacement /µm')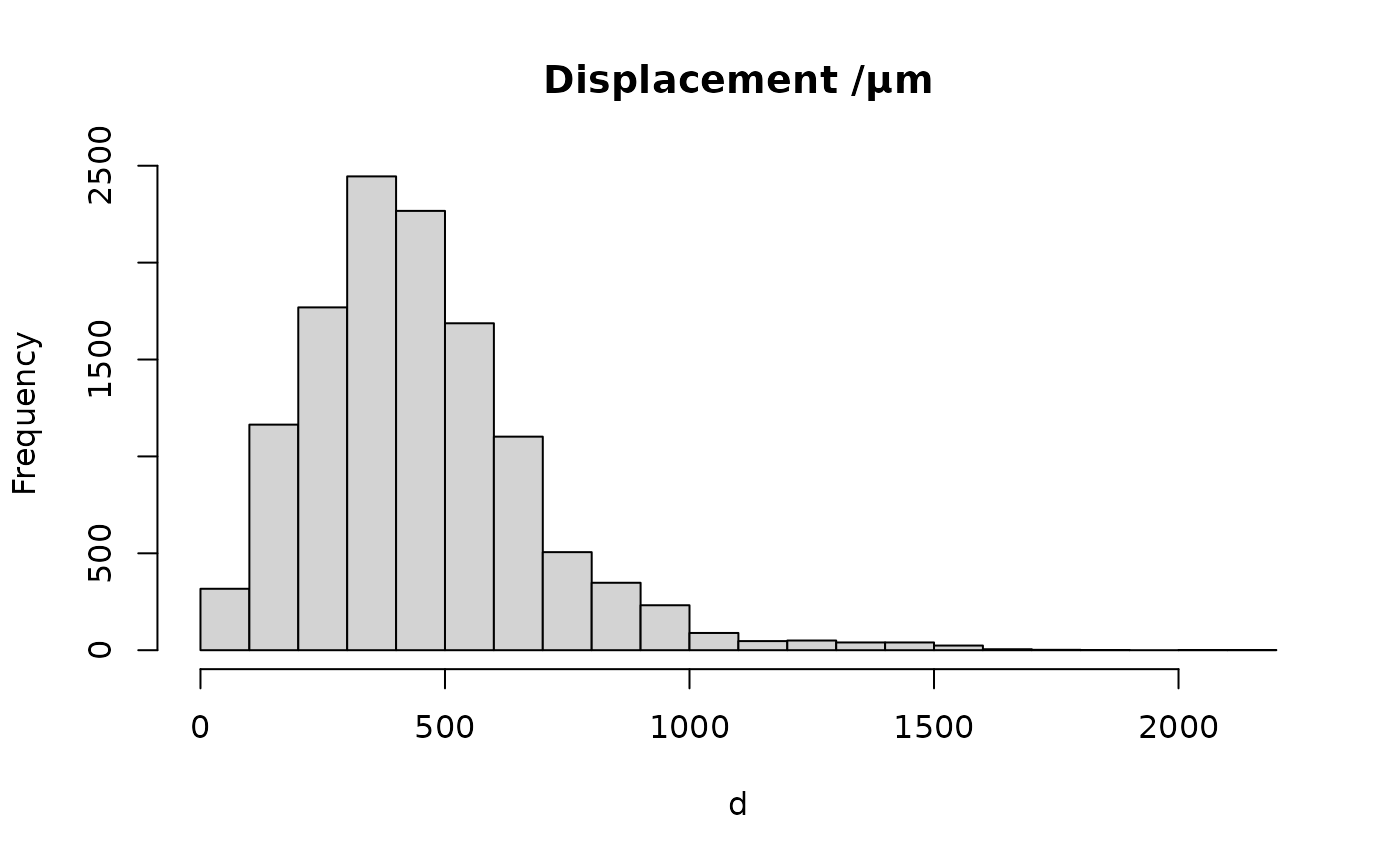
sample_points_in_surf <- function(x, n){
x=as.mesh3d(x)
bb=boundingbox(x)
mm=mapply(runif, min=bb[1,], max=bb[2,], n = n)
colnames(mm)=c("X","Y","Z")
data.frame(mm, inside=pointsinside(mm,x))
}Round trip error
Let’s send those points back again
sxyz.fafb2=flywire2fafb(sxyz.fw)
deltas=sxyz.fafb2-xyzmatrix(sxyz.in)
delta=rowSums(deltas[,c("X","Y")])
hist(delta, main = "Round Trip Error", xlab='delta /nm')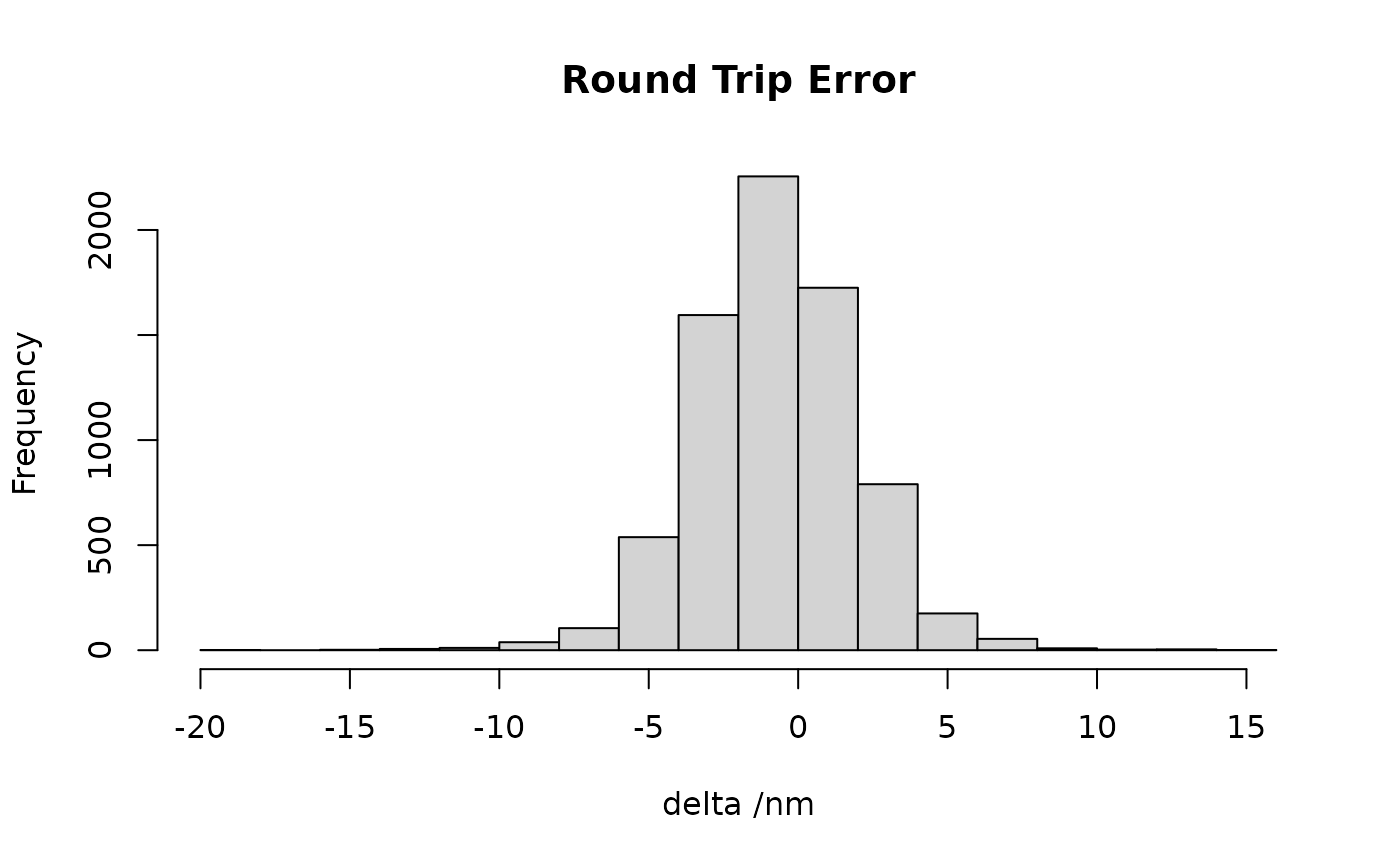
Mapping anything
To map complex objects, use xform_brain()
AV4b1.fw=xform_brain(AV4b1, sample='FAFB14', reference = 'FlyWire')
# find the main branch point of a neuron, a good place to point to
mainbranch <- function(x, ...) {
if(is.neuronlist(x))
return(nlapply(x, mainbranch, ...))
sx=nat::simplify_neuron(x, ...)
xyzmatrix(sx)[sx$BranchPoints,]
}
choose_segmentation("flywire")
open_fafb_ngl(mainbranch(AV4b1.fw), coords.only = TRUE)
#> Warning: The `father` argument of `dfs()` is deprecated as of igraph 2.2.0.
#> ℹ Please use the `parent` argument instead.
#> ℹ The deprecated feature was likely used in the nat package.
#> Please report the issue at <https://github.com/natverse/nat/issues>.
#> This warning is displayed once every 8 hours.
#> Call `lifecycle::last_lifecycle_warnings()` to see where this warning was
#> generated.
#> [1] "88371.25,40478.75,3668"
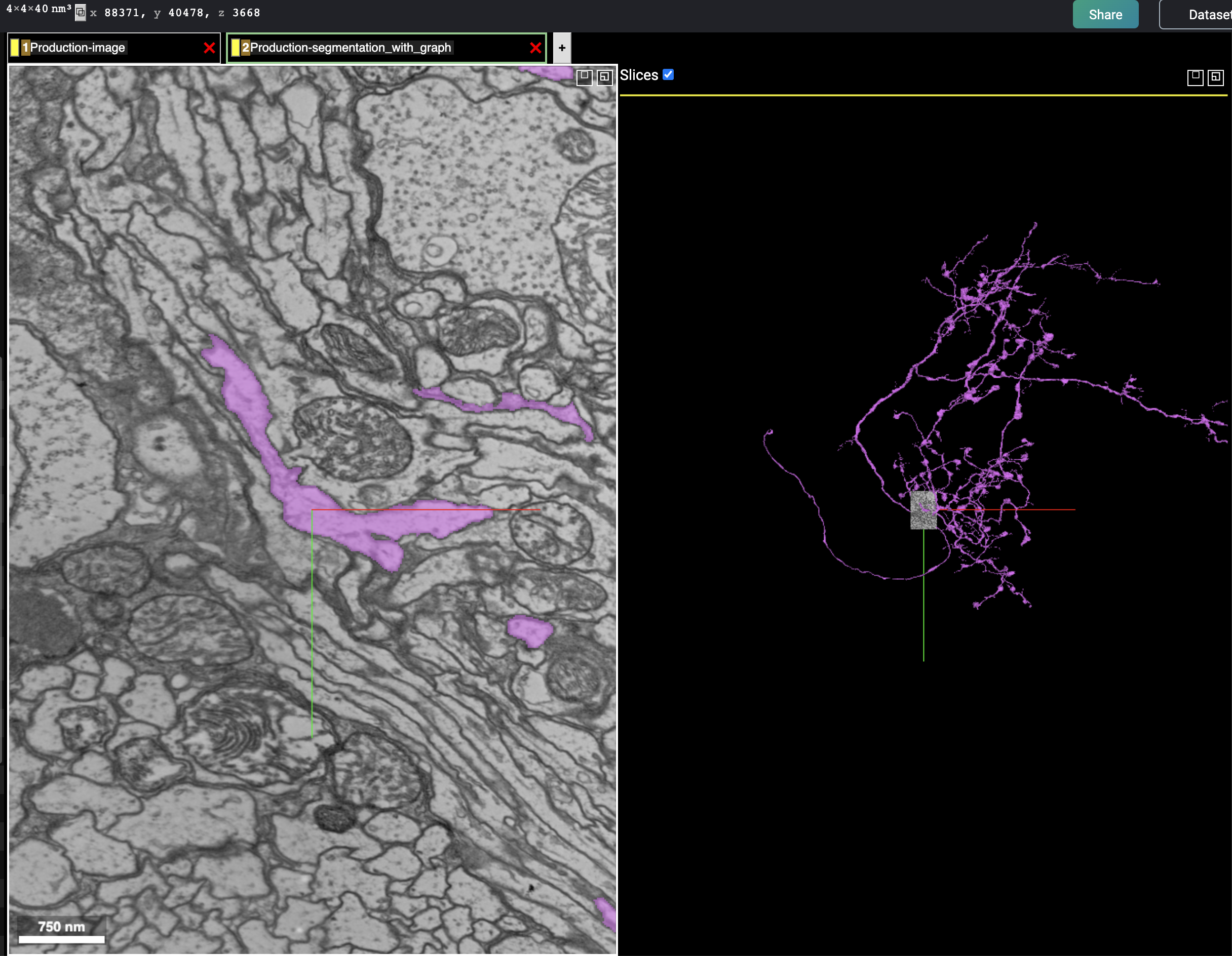
Note the relevant links:
Load the flywire mesh
av4.fwm=read_cloudvolume_meshes('720575940618054533')And plot with the CATMAID skeleton
wire3d(av4.fwm[[1]], col='grey', alpha=.2)